Details Of Published TSH Receptor Mutation
Met 626 Ile
c.1877G>CConstitutively Activating TSH Receptor Mutation
Type
gain
Manifestation
family
Exon
10
Legend:

Male

Female

Unknown

Deceased
+
Mutation
-
No Mutation

Hyperthyroidism
(Heterozygous)
(Heterozygous)

Goiter

Relapse
P
Index Patient
Molecular Characteristics:
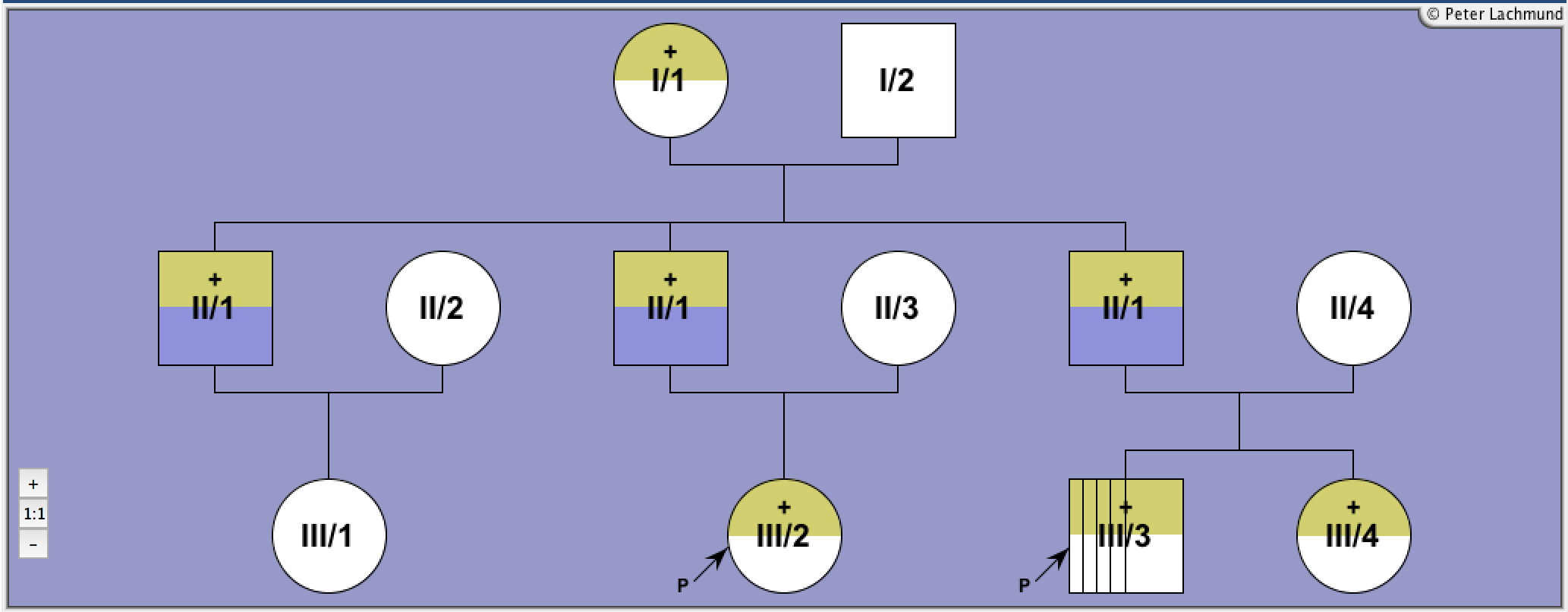
Family 1: Pedigree 1: Ringkananont et al. (Pedigree 1)
Note:
Blue marked individuals are identical (II/1 is married twice)
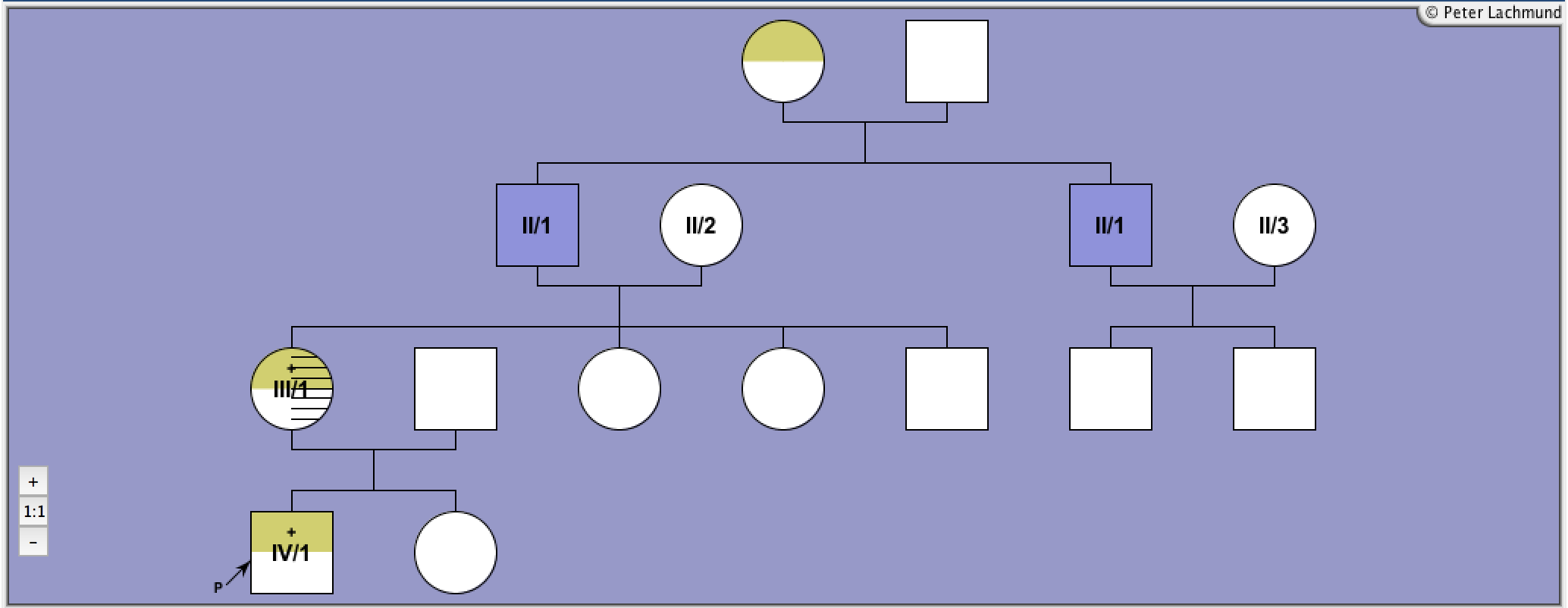
Familiy 2: Pedigree 2: Jäschke et al.
Note:
Blue marked individuals are identical (II/1 is married three times)
Note:
Blue marked individuals are identical (II/1 is married twice)
Familiy 2: Pedigree 2: Jäschke et al.
Note:
Blue marked individuals are identical (II/1 is married three times)
Clinical Features:
Family 1 - Pedigree 1 (Ringkananont et al.):
diagnosis:
P1/III/2: 10 months (index patient)
P1/III/3: 15 months (index patient)
P1/III/4: neonatal
P1/II/1: 30 yr
P1/I/1: hyperthyroidism
Familiy 2 - Pedigree 2 (Jäschke et al.):
diagnosis:
P2/III/1: 10 yr
P2/IV/1: 6 weeks
* based on 2 activating familial germline mutations investigated by Ringkananont et al. 2006 and Jäschke et al. 2011
diagnosis:
P1/III/2: 10 months (index patient)
P1/III/3: 15 months (index patient)
P1/III/4: neonatal
P1/II/1: 30 yr
P1/I/1: hyperthyroidism
Familiy 2 - Pedigree 2 (Jäschke et al.):
diagnosis:
P2/III/1: 10 yr
P2/IV/1: 6 weeks
* based on 2 activating familial germline mutations investigated by Ringkananont et al. 2006 and Jäschke et al. 2011
Treatment:
Family 1 - Pedigree 1 (Ringkananont et al.):
P1/III/2: antithyoid medication
P1/I/1: subtotal TE
Familiy 2 - Pedigree 2 (Jäschke et al.):
P2/III/1: antithyroid medication for 2yrs, relapse after withdrawal, radioiodine therapy (7mCi, 12mCi) at 14yrs, euthyroid with L-T4
P1/III/2: antithyoid medication
P1/I/1: subtotal TE
Familiy 2 - Pedigree 2 (Jäschke et al.):
P2/III/1: antithyroid medication for 2yrs, relapse after withdrawal, radioiodine therapy (7mCi, 12mCi) at 14yrs, euthyroid with L-T4
Functional Characteristics:
cAMP
(basal)
(basal)
cAMP
(TSH)
(TSH)
IP
(basal)
(basal)
IP
(TSH)
(TSH)
TSH-Binding
Cell Surface Expression
Prevalence
LRA
Ref
3.5-4.9
1.0
1.0
1.3
0.3-0.7
2
6.8±0.4
1,2
Legend:
cAMP (basal): basal in vitro cAMP production of mutant over wild-type TSHR
cAMP (TSH): maximal in vitro cAMP production of mutant over wild-type TSHR
IP (basal): basal in vitro IP production of mutant over wild-type TSHR
IP (TSH): maximal in vitro IP production of mutant over wild-type TSHR
TSH-binding: maximal TSH-binding compared to the wild-type TSHR
Cell surface expression: cell surface expression of mutant compared to WT-TSHR
LRA: linear regression analysis (LRA) of constitutive activity as a function of TSHR expression determined by 125I-bTSH binding or FACS analysis compared to the wild-type TSHR
Prevalence: Prevalence of (somatic and germline) activating mutations*
Ref: Reference for functional characterization
Child: Found in children.
Reference 1:
Ringkananont et al.
Mol Endocrinol. 20: 893-903
Repulsive separation of the cytoplasmic ends of transmembrane helices 3 and 6 is linked to receptor activation in a novel thyrotropin receptor mutant (M626I).
2006
Reference 2:
Jäschke et al.
Horm Metab Res. 43:500-4
Prolonged inappropriate TSH suppression during hypothyroidism after thyroid ablation in a patient with nonautoimmune familial hyperthyroidism.
2011