Details Of Published TSH Receptor Mutation
Arg 109 Gln
c.326G>AInactivating TSH Receptor Mutation
Type
loss
Manifestation
family
Exon
4
Legend:

Male

Female

Unknown

Deceased
+
Mutation
-
Wild-Type

Heterozygous

Heterozygous

Compound Heterozygous

Homozygous

Hypothyroid

Hypoplastic Gland + Hypothyroid
P
Index Patient
Molecular Characteristics:
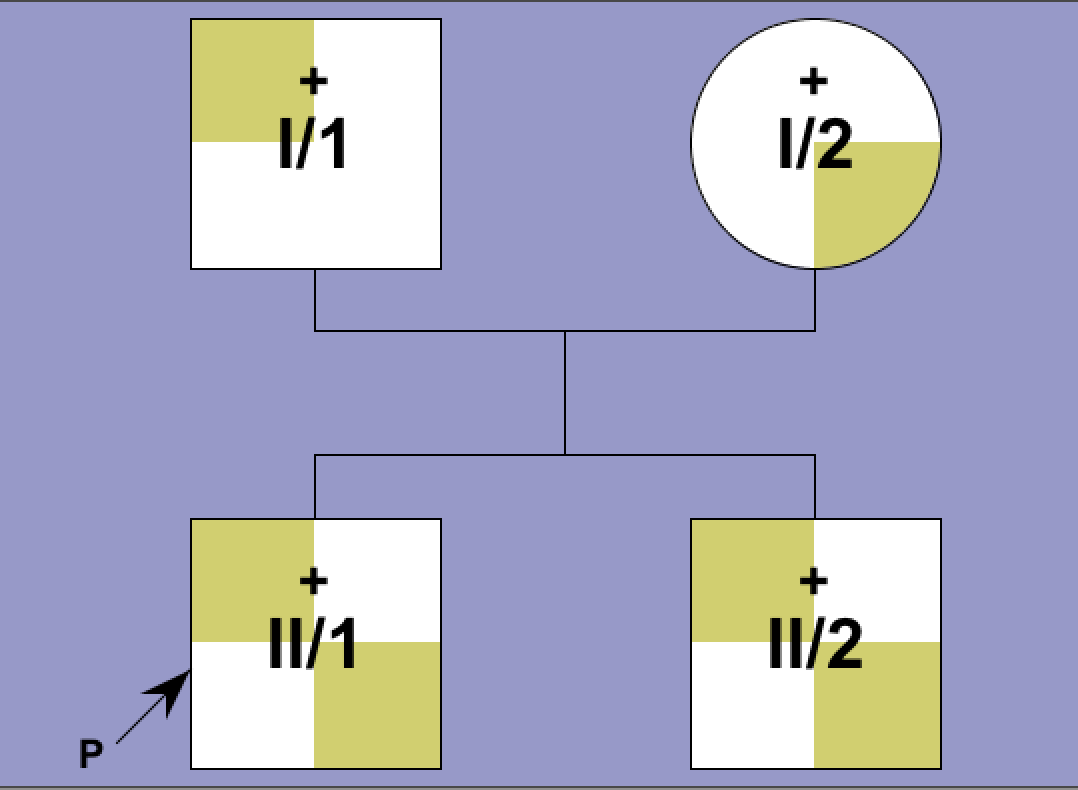
Family 1 - Pedigree 1 (Clifton-Bilgh et al.):
I/1: Arg109Gln
I/2: Trp546Stop
II/1-2: Arg109Gln/Trp546Stop compound heterozygous
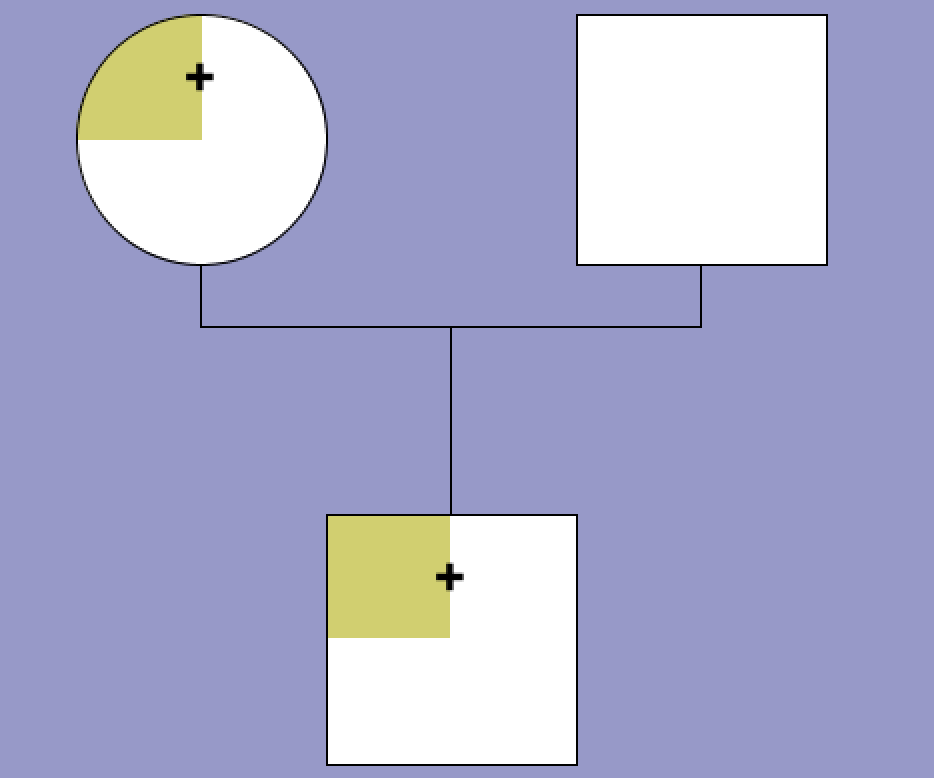
Family 2 - Pedigree 2 (Nicoletti et al.):
propositus and mother heterozygous
Family 3: heterozygous, 2 brothers
I/1: Arg109Gln
I/2: Trp546Stop
II/1-2: Arg109Gln/Trp546Stop compound heterozygous
Family 2 - Pedigree 2 (Nicoletti et al.):
propositus and mother heterozygous
Family 3: heterozygous, 2 brothers
Clinical Features:
Family 1 - Pedigree 1 (Clifton-Bilgh et al.):
diagnosis:
II/1: 8 weeks
II/2: neonatal, borderline hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism under L-thyroxine treatment, normal thyroid gland on ultrasound, normal sciniscan
Family 2 - Pedigree 2 (Nicoletti et al.):
normal thyroid size
Family 3 (Cerbone et al.)
permanent congenital hypothyroidism
diagnosis:
II/1: 8 weeks
II/2: neonatal, borderline hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism under L-thyroxine treatment, normal thyroid gland on ultrasound, normal sciniscan
Family 2 - Pedigree 2 (Nicoletti et al.):
normal thyroid size
Family 3 (Cerbone et al.)
permanent congenital hypothyroidism
Treatment:
Family 1 - Pedigree 1 (Clifton-Bilgh et al.):
none since hyperthyroid under L-thyroxine
none since hyperthyroid under L-thyroxine
Functional Characteristics:
cAMP
(basal)
(basal)
cAMP
(TSH)
(TSH)
IP
(basal)
(basal)
IP
(TSH)
(TSH)
TSH-Binding
Cell Surface Expression
Prevalence
LRA
Ref
~
+
nd
nd
+
nd
3
Legend:
cAMP (basal): basal in vitro cAMP production of mutant over wild-type TSHR
cAMP (TSH): maximal in vitro cAMP production of mutant over wild-type TSHR
IP (basal): basal in vitro IP production of mutant over wild-type TSHR
IP (TSH): maximal in vitro IP production of mutant over wild-type TSHR
TSH-binding: maximal TSH-binding compared to the wild-type TSHR
Cell surface expression: cell surface expression of mutant compared to WT-TSHR
LRA: linear regression analysis (LRA) of constitutive activity as a function of TSHR expression determined by 125I-bTSH binding or FACS analysis compared to the wild-type TSHR
Prevalence: Prevalence of (somatic and germline) activating mutations*
Ref: Reference for functional characterization
Child: Found in children.
Reference 1:
Clifton-Bligh et al.
J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metabol. 82: 1094-1100
Two novel mutations in the thyrotropin (TSH) receptor gene in a child with resistance to TSH
1997
Reference 2:
Nicoletti et al.
J Clin Endocrinol Metab 94:4187-4194.
Thyrotropin-stimulating hormone receptor gene analysis in pediatric patients with non-autoimmune subclinical hypothyroidism.
2009
Reference 3:
Cerbone, Manuela, et al.
Italian journal of pediatrics
Non-autoimmune subclinical hypothyroidism due to a mutation in TSH receptor: report on two brothers.
2013