Details Of Published TSH Receptor Mutation
Pro 162 Ala
c.484C>GInactivating TSH Receptor Mutation
Type
loss
Manifestation
family
Exon
6
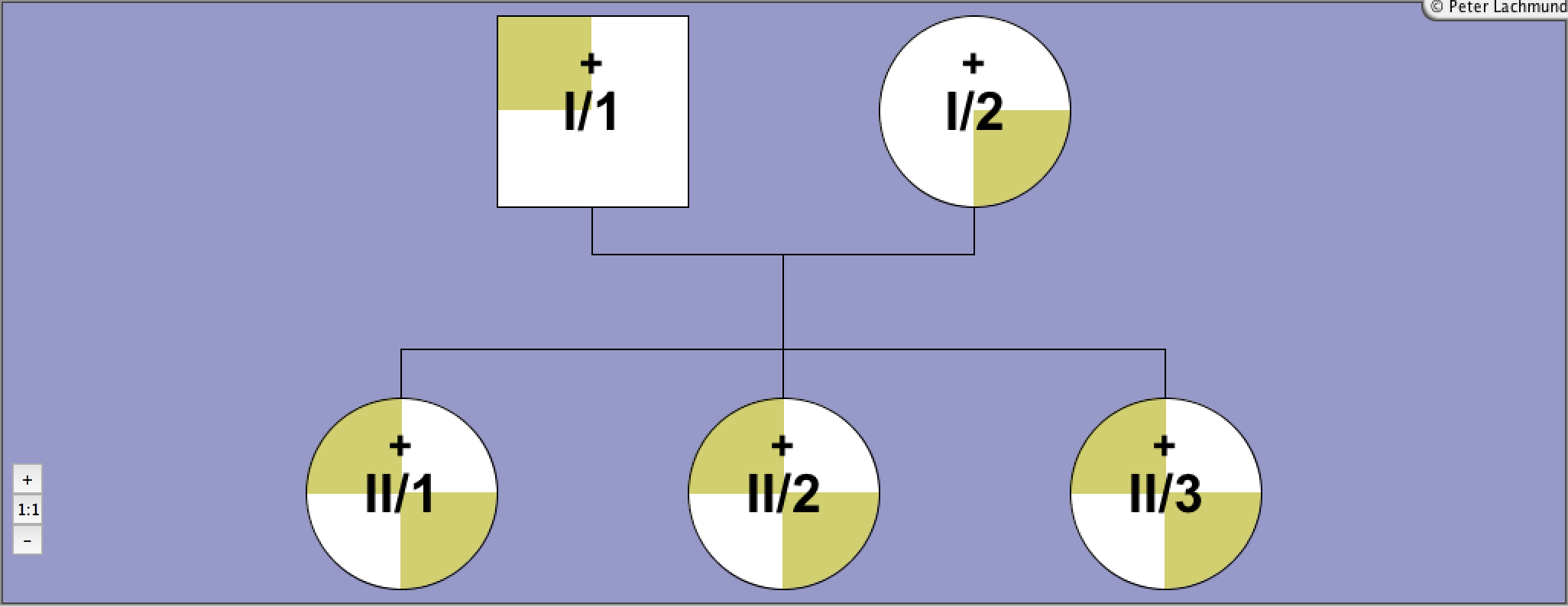
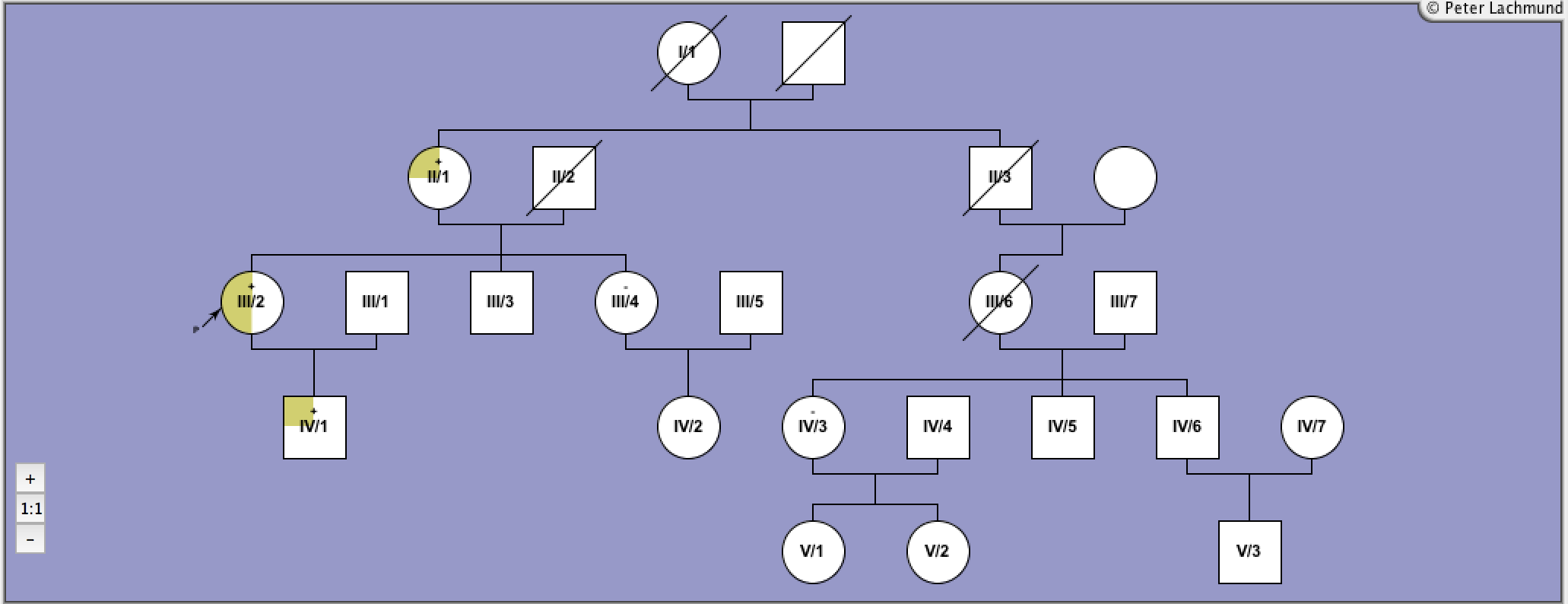
Pedigree 1 - Sunthornthepvarakui et al.
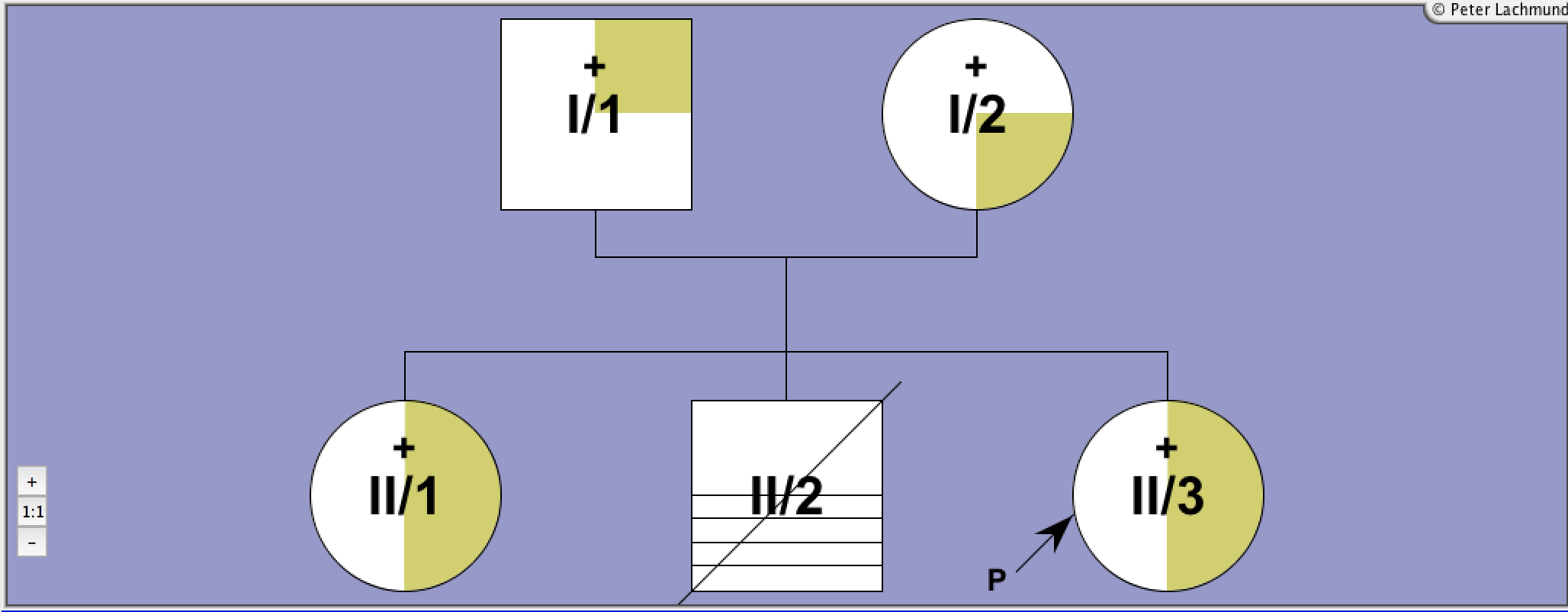
Pedigree 2 - De Roux et al.
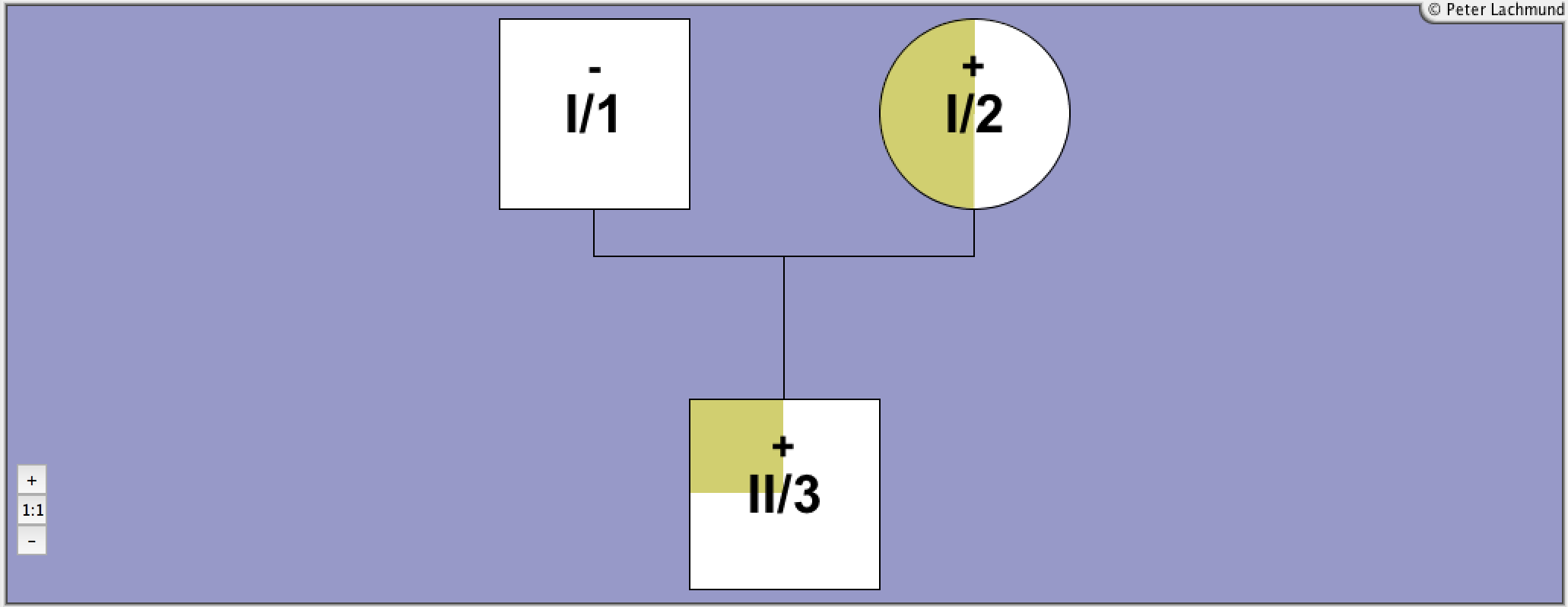
Pedigree 3 - Tonacchera et al. 2001
Pedigree 4 - Tonacchera et al. 2007
Pedigree 5 - Tonacchera et al. 2004
Pedigree 6 - Nicoletti et al.
Pedigree 7 - Alberti et al.
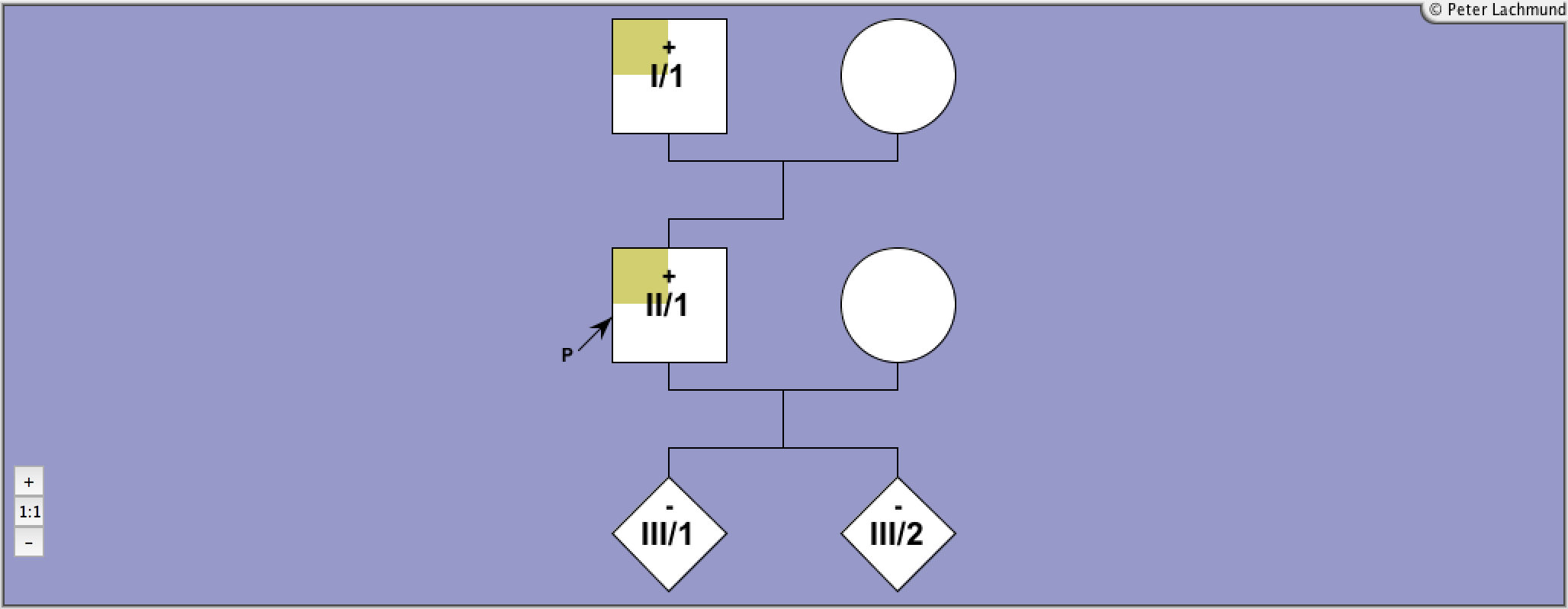
Labadi et al.
Legend:

Male

Female

Unknown

Deceased
+
Mutation
-
Wild-Type

Heterozygous

Heterozygous

Compound Heterozygous

Homozygous

Hypothyroid

Hypoplastic Gland + Hypothyroid
P
Index Patient
Molecular Characteristics:
Family 1 - pedigree 1 (Sunthornthepvaraku et al.):
I/1: Ile167Asn
I/2: Pro162Ala/Pro52Thr
II/1-3: Pro162Ala/Ile167Asn
compound heterozygous
polymorphism Pro52Thr in I/2
Family 2 - pedigree 2 (de Roux et al.):
I/1: Pro162Ala
I/2: Pro162Ala (consanguinous)
II/3: Pro162Ala homozygous
II/1: Pierre-Robin syndrome
II/2: Down's syndrome
Family 3 - pedigree 3 (Tonacchera et al. 2001):
I/1: polymorphism Pro52Thr
I/2: Pro162Ala/Pro162Ala
II/1: Pro162Ala
compound heterozygous
polymorphism Pro52Thr
Family 4 - pedigree 4 (Tonacchera et al. 2007):
proband and father: heterozygous for P162A, and P52T polymorphism
two children: wild type
Family 5 - pedigree 5 (Tonacchera et al. 2004):
III/2 proband: homozygous, consanguineous parents
II/2: mother heterozygous
IV/2: son: heterozygous
II/1 and II/3, II/3 and II/4: consanguinous parents
Family 6 - pedigree 6 (Nicoletti et al.):
propositus and father heteroz.
Family 7 - pedigree 7 (Alberti et al.):
I/1: Cys600Arg
I/2: P162Ala
II/1: Cys600Arg/P162Ala compound heterozygous
II/2: Pro162Ala
Family 8 - pedigree 8 (Camilot et al.):
son: homozygous
sister, parents heterozygous for P162A
1 non related child heterozygous
Family 9: P162S/R450H
I/1: Ile167Asn
I/2: Pro162Ala/Pro52Thr
II/1-3: Pro162Ala/Ile167Asn
compound heterozygous
polymorphism Pro52Thr in I/2
Family 2 - pedigree 2 (de Roux et al.):
I/1: Pro162Ala
I/2: Pro162Ala (consanguinous)
II/3: Pro162Ala homozygous
II/1: Pierre-Robin syndrome
II/2: Down's syndrome
Family 3 - pedigree 3 (Tonacchera et al. 2001):
I/1: polymorphism Pro52Thr
I/2: Pro162Ala/Pro162Ala
II/1: Pro162Ala
compound heterozygous
polymorphism Pro52Thr
Family 4 - pedigree 4 (Tonacchera et al. 2007):
proband and father: heterozygous for P162A, and P52T polymorphism
two children: wild type
Family 5 - pedigree 5 (Tonacchera et al. 2004):
III/2 proband: homozygous, consanguineous parents
II/2: mother heterozygous
IV/2: son: heterozygous
II/1 and II/3, II/3 and II/4: consanguinous parents
Family 6 - pedigree 6 (Nicoletti et al.):
propositus and father heteroz.
Family 7 - pedigree 7 (Alberti et al.):
I/1: Cys600Arg
I/2: P162Ala
II/1: Cys600Arg/P162Ala compound heterozygous
II/2: Pro162Ala
Family 8 - pedigree 8 (Camilot et al.):
son: homozygous
sister, parents heterozygous for P162A
1 non related child heterozygous
Family 9: P162S/R450H
Clinical Features:
Family 1 - pedigree 1 (Sunthornthepvarakui et al.):
diagnosis:
II/1: 4yr
II/2: neonatal
II/3: neonatal, euthyroid hyperthyrotropinaemia, normal scintiscan
I/1 and I/2: borderline TSH levels
Family 2 - pedigree 2 (de Roux et al.):
diagnosis:
II/3: neonatal, euthyroid hyperthyrotropinaemia, normal gland on 123-I scan
Family 3 - pedigree 3 (Tonacchera et al. 2001):
diagnosis:
I/2: 47yr, euthyroid hyperthyrotropinaemia, normal gland on ultrasound development of hypothyroidism with concomittant autoimmune thyroid disease
II/1: borderline TSH levels
Family 4 - pedigree 4 (Tonacchera et al. 2007):
II/1: 38yr male, hyperthyrotropinaemia, Ab negative
thyroid: no goiter, normal ultrasound pattern
I/1: TSH elevated
III/1, III/2 normal thyroid function
Family 5 - pedigree 5 (Tonacchera et al. 2004):
prop: 47yr woman, neck discomfort, isolated hyperthyrotropinemia, no sings of hypothyroidism
mother: TSH elevated
son: euthyroid 23yrs, basal TSH elevated
III/3 4 sister and brother: normal thyroid tests
IV/2 daughter of the sister: TSH elevated
IV/3: normal, daughter: V/1: TSH elevated, TPOAb and TgAb pos. chron. autoimmune thyroiditis
Family 6 - pedigree 6 (Nicoletti et al.):
prop: hypoplastic thyroid, growth retardation
Family 7 - pedigree 7 (Alberti et al.):
diagnosis:
II/1: 25yr, euthyroid hyperthyrotropinaemia, hypoplastic thyroid gland, 1 brother and parents with borderline TSH levels
Family 8 - pedigree 8 (Camilot et al.:)
son: hypothyroid newborn, eutopic thyroid gland, Ab negative, sister subclinical hypothyrodism
1 non related child with subclinical hypothyrodism, heterozygous
Family 9: Vigone et al. P162A siblings with heterozygous mutation, no parental data thus familial assumed
diagnosis:
II/1: 4yr
II/2: neonatal
II/3: neonatal, euthyroid hyperthyrotropinaemia, normal scintiscan
I/1 and I/2: borderline TSH levels
Family 2 - pedigree 2 (de Roux et al.):
diagnosis:
II/3: neonatal, euthyroid hyperthyrotropinaemia, normal gland on 123-I scan
Family 3 - pedigree 3 (Tonacchera et al. 2001):
diagnosis:
I/2: 47yr, euthyroid hyperthyrotropinaemia, normal gland on ultrasound development of hypothyroidism with concomittant autoimmune thyroid disease
II/1: borderline TSH levels
Family 4 - pedigree 4 (Tonacchera et al. 2007):
II/1: 38yr male, hyperthyrotropinaemia, Ab negative
thyroid: no goiter, normal ultrasound pattern
I/1: TSH elevated
III/1, III/2 normal thyroid function
Family 5 - pedigree 5 (Tonacchera et al. 2004):
prop: 47yr woman, neck discomfort, isolated hyperthyrotropinemia, no sings of hypothyroidism
mother: TSH elevated
son: euthyroid 23yrs, basal TSH elevated
III/3 4 sister and brother: normal thyroid tests
IV/2 daughter of the sister: TSH elevated
IV/3: normal, daughter: V/1: TSH elevated, TPOAb and TgAb pos. chron. autoimmune thyroiditis
Family 6 - pedigree 6 (Nicoletti et al.):
prop: hypoplastic thyroid, growth retardation
Family 7 - pedigree 7 (Alberti et al.):
diagnosis:
II/1: 25yr, euthyroid hyperthyrotropinaemia, hypoplastic thyroid gland, 1 brother and parents with borderline TSH levels
Family 8 - pedigree 8 (Camilot et al.:)
son: hypothyroid newborn, eutopic thyroid gland, Ab negative, sister subclinical hypothyrodism
1 non related child with subclinical hypothyrodism, heterozygous
Family 9: Vigone et al. P162A siblings with heterozygous mutation, no parental data thus familial assumed
Treatment:
L-thyroxine
Functional Characteristics:
cAMP
(basal)
(basal)
cAMP
(TSH)
(TSH)
IP
(basal)
(basal)
IP
(TSH)
(TSH)
TSH-Binding
Cell Surface Expression
Prevalence
LRA
Ref
-
+
nd
nd
+
-
13
Legend:
cAMP (basal): basal in vitro cAMP production of mutant over wild-type TSHR
cAMP (TSH): maximal in vitro cAMP production of mutant over wild-type TSHR
IP (basal): basal in vitro IP production of mutant over wild-type TSHR
IP (TSH): maximal in vitro IP production of mutant over wild-type TSHR
TSH-binding: maximal TSH-binding compared to the wild-type TSHR
Cell surface expression: cell surface expression of mutant compared to WT-TSHR
LRA: linear regression analysis (LRA) of constitutive activity as a function of TSHR expression determined by 125I-bTSH binding or FACS analysis compared to the wild-type TSHR
Prevalence: Prevalence of (somatic and germline) activating mutations*
Ref: Reference for functional characterization
Child: Found in children.
Reference 1:
Sunthornthepvarakui et al.
N. Engl. J. Med. 332: 155-157
Brief report: resistance to thyrotropin caused by mutations in the thyrotropin-receptor gene
1995
Reference 2:
De Roux et al.
J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metabol. 81: 4229-4235
Four families with loss of function mutations of the thyrotropin receptor
1996
Reference 3:
Tonacchera et al.
J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 86: 4543-4546
Thyroid Resistance to TSH Complicated by Autoimmune Thyroiditis
2001
Reference 4:
Costagliola et al.
Thyroid 9: 995-1000
Structure-function relationships of two loss-of-function mutations of the thyrotropin receptor gene
1999
Reference 5:
Calebiro et al.
J Clin Endocrinol Metab 97:156-160.
Frequent TSH Receptor Genetic Alterations with Variable Signaling Impairment in a Large Series of Children with Nonautoimmune Isolated Hyperthyrotropinemia.
2012
Reference 6:
Camilot et al.
Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 63:146-151.
Thyrotropin receptor gene mutations and TSH resistance: variable expressivity in the heterozygotes.
2005
Reference 7:
Cangul et al.
Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 73:671-677.
Novel TSHR mutations in consanguineous families with congenital nongoitrous hypothyroidism.
2010
Reference 8:
Nicoletti et al.
J Clin Endocrinol Metab 94:4187-4194.
Thyrotropin-stimulating hormone receptor gene analysis in pediatric patients with non-autoimmune subclinical hypothyroidism.
2009
Reference 9:
Tonacchera et al.
J Clin Endocrinol Metab 89:5787-5793.
Low prevalence of thyrotropin receptor mutations in a large series of subjects with sporadic and familial nonautoimmune subclinical hypothyroidism.
2004
Reference 10:
Tonacchera et al.
Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 67:712-718.
Identification of TSH receptor mutations in three families with resistance to TSH.
2007
Reference 11:
Ba?, Veysel Nijat, et al.
Journal of Pediatric Endocrinology and Metabolism
Mild and severe congenital primary hypothyroidism in two patients by thyrotropin receptor (TSHR) gene mutation.
2012
Reference 12:
Lábadi, Árpád, et al.
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism
Loss-of-function variants in a Hungarian cohort reveal structural insights on TSH receptor maturation and signaling
2015
Reference 13:
Vigone et al.
Clinical Endocrinology
Mild TSH resistance: Clinical and hormonal features in childhood and adulthood
2017